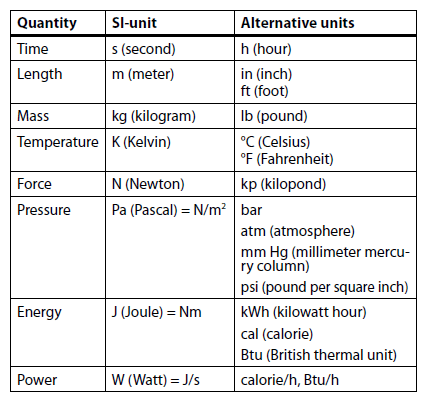
Fundamental terms
On an international level, the use of the Systeme International d’Unités is used in refrigeration. This is often referred to as the SI-system. For a number of countries the implementation of the SI-system is still an on-going process. However, in many parts of the refrigeration community metric units or other alternative units are still used (the practically used alternative units will be shown in brackets). The table shows the SI-units and the other often used alternative units.
Temperature
Temperature is a very important part of refrigeration. Almost all refrigeration systems are for the purpose of reducing the temperature of an object like the air in a room or the objects stored in that room. The SI-unit for temperature Kelvin [K] is an absolute temperature because its reference point [0 K] is the lowest temperature that it in theory would be able to obtain.
When working with refrigeration systems the temperature unit degree Celsius [°C] is a more practical unit to use. Celsius is not an absolute temperature scale because its reference point (0 °C) is defined by the freezing point of water (equal to 273.15 K). The only difference between Kelvin and Celsius is the difference in reference point. This means that a temperature difference of 1 °C is exactly the same as a temperature difference of 1 K. In the scientific part of the refrigeration community temperature differences are often described using [K] instead of [°C]. This practice eliminates the possible mix-up of temperatures and temperature differences.